
Welcome to our Steel Wire Rope Properties Guide! This site is designed to help you understand the various icons found on our product pages and what they signify. Here, you'll find detailed explanations of key SWR properties, including material types like stainless steel and galvanized, lay directions, and specialized manufacturing processes such as compacted, parallel, rotary swaged and rotation resistant ropes. Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge needed to select the right steel wire rope for your specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Explore the icons and learn about the unique characteristics that make each rope suitable for different environments and tasks.
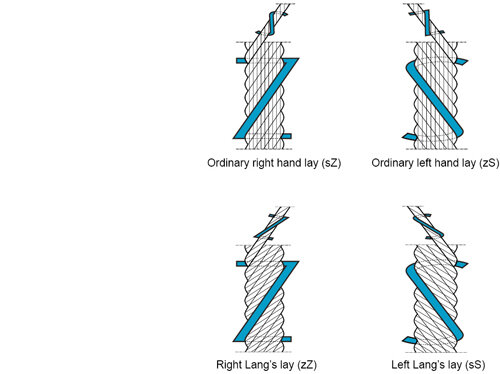
Rope lays
The terms refer to the direction in which the strands and wires of a steel wire rope are twisted. These different rope lays affect the rope's performance characteristics, including flexibility, resistance to rotation, and suitability for specific applications.
These directions are indicated by specific symbols. Here are the definitions for each:
S (Left Lay):
|
|
sS (Left Lay, Left-Hand Twist):
|
|
sZ (Left Lay, Right-Hand Twist):
|
Z (Right Lay):
|
|
zS (Right Lay, Left-Hand Twist):
|
|
zZ (Right Lay, Right-Hand Twist):
|
Rope Finishes
The terms refer to different types of protective coatings applied to steel wire ropes to enhance their resistance to corrosion.
GalvanizedDefinition: Galvanized steel wire ropes are coated with a layer of zinc through a process called galvanization. This zinc coating provides a protective barrier against corrosion. Properties:
Applications: Galvanized ropes are commonly used in construction, agriculture, marine applications, and general-purpose lifting and rigging. |
|
Heavy-GalvanizedDefinition: Heavy-Galvanized steel wire ropes have a thicker layer of zinc coating compared to standard galvanized ropes. This thicker coating provides enhanced protection against corrosion. Properties:
Applications: Heavy-galvanized ropes are used in applications where maximum corrosion resistance is required, such as in marine, industrial, and outdoor settings with high exposure to moisture and chemicals. |
Stainless steelDefinition: Stainless steel wire ropes are made from stainless steel, which is an alloy containing chromium and other elements that enhance its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Properties:
Applications: Stainless steel ropes are commonly used in marine environments, food processing industries, medical equipment, architectural applications, and other settings where corrosion resistance and durability are critical. They are also used in outdoor installations, such as bridges and railings, where both strength and appearance are important. |
|
Ungalvanized/BlankDefinition: Ungalvanized steel wire ropes are made from steel without any protective zinc coating. These ropes lack additional corrosion protection and are therefore more susceptible to rust and corrosion. Properties:
Applications: Ungalvanized ropes are commonly used in indoor applications, temporary constructions, and situations where corrosion protection is not necessary. They can also be used in applications where the rope is not exposed to moisture or aggressive chemicals. |
Steel wire rope designed for swivel
Approved width swivel |
Not approved with swivel |
Manufacturing Processes and Design Characteristics
These terms describe specific methods and structural designs used to enhance the performance and suitability of steel wire ropes for various applications.
CompactedThe term in the context of steel wire rope properties refers to a specific manufacturing process where the individual wires or strands of the rope are compressed or compacted. This process results in several key benefits:
Overall, "Compacted" steel wire ropes are designed to offer superior performance in terms of strength, durability, and efficiency, making them suitable for heavy-duty lifting and rigging applications. |
|
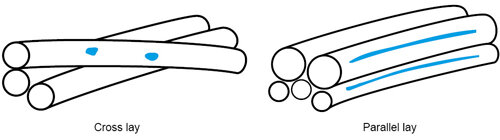
ParallelThe term in steel wire rope properties refers to a specific strand design where all the wires within the strands are laid parallel to each other. This design avoids crossovers between the wires, resulting in line contact rather than point contact. The parallel lay design offers several advantages:
|
Rotary SwagedThe term in steel wire rope properties refers to a specific manufacturing process where the rope is hammered or compressed using a rotary swaging machine. This process results in several key benefits:
|
|
Rotation ResistantThe term in steel wire rope properties refers to a specific design that minimizes the rope's tendency to rotate under load. This is achieved by constructing the rope with an independent wire rope core (IWRC) and outer strands that are closed in the opposite direction. The moments generated by the IWRC and the outer strands counteract each other, resulting in a rope that does not twist or rotate when subjected to an axial load. The key benefits of rotation-resistant ropes include:
|

Which steel wire rope fits where?
Some icons indicate the type of application the steel wire rope is intended for. The icons below explain:
| Agriculture | Container crane | Crawler crane | Deck crane |
| Elevator | General use | Heavy lift crane | Jib crane |
| Knuckle boom crane | Ladle crane | Loading crane | Luffing crane |
| Mobile crane | Mobile port crane | Offshore crane | Overhead crane |
| Overhead line | Piling crane | RTG crane | Self-erecting crane |
| Sling | Stay rope | Straddle carrier | STS crane |
| Tower crane | Truck crane | Winch |
| Limitador typically refers to a device or mechanism that limits certain parameters, such as load, movement, or speed, to ensure safe operation and prevent overloading or other hazardous conditions. |
Do you wish to know more about our Lifting KnowHow? Please reach out.
For faster response, call us directly at +47 66 79 95 00!
Composition of steel wire ropeLearn more about the composition of steel wire rope. |
Learn more |
Diameter and tolerance of steel wire ropeLearn more about tolerance of steel wire rope. |
Learn more |
Discarding of steel wire ropeLearn more about the correct ways of discarding steel wire rope. |
Learn more |
Factors to consider when selecting your wire ropeLearn more about how to choose the right steel wire rope. |
Learn more |
Installation of steel wire ropeLearn more about installation of your steel wire rope. |
Learn more |
Technical description of steel wire ropeLearn more about steel wire rope applications. |
Learn more |
Understanding our steel wire rope iconsLearn about the icons found on our steel wire rope product pages. Understanding them can be crucial when picking the right rope. |
Learn more |


